Tri 1 Final Mcq Practice Blog
Shreya Sapkal
Period 3
Tri 1 Final MCQ Practice Blog
-
Q8: Documentation for procedure with lists
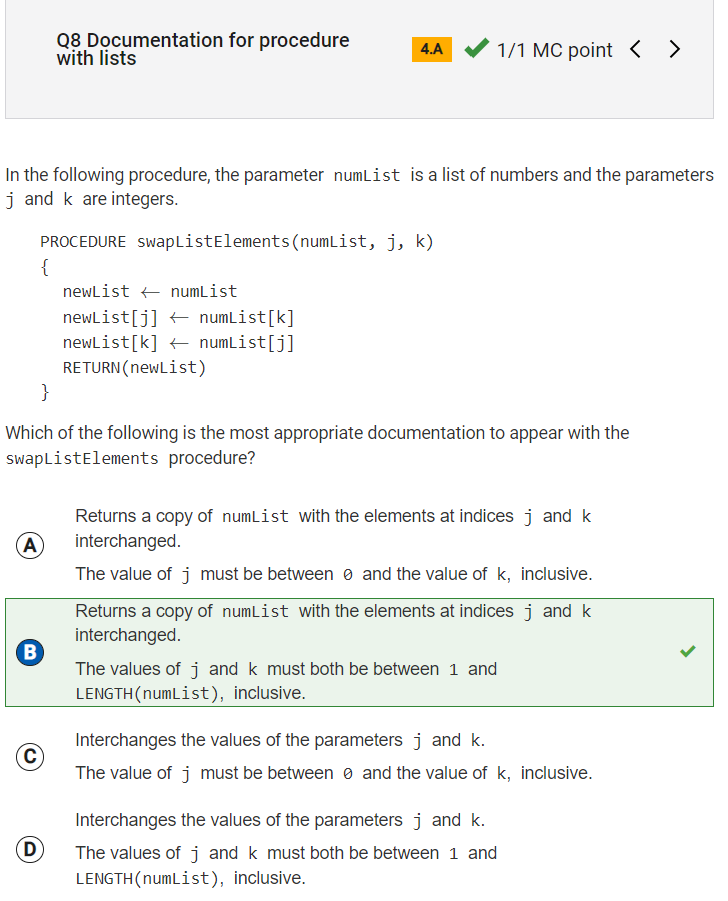
Reflection: This problem was confusing to me. I understood that a newList is created out of the numList, and that the elements at indices j and k are interchanged. I didn’t understand the second half of the problem, so I reviewed the collegeboard explanation. The explanation helped me understand that the procedure can only work if j and k are valid indices, and in order for the indices to be valid, the values of j and k must be between 1 and the length of the original numList [LENGTH(numList)].
-
Q17: Purpose of Internet protocols
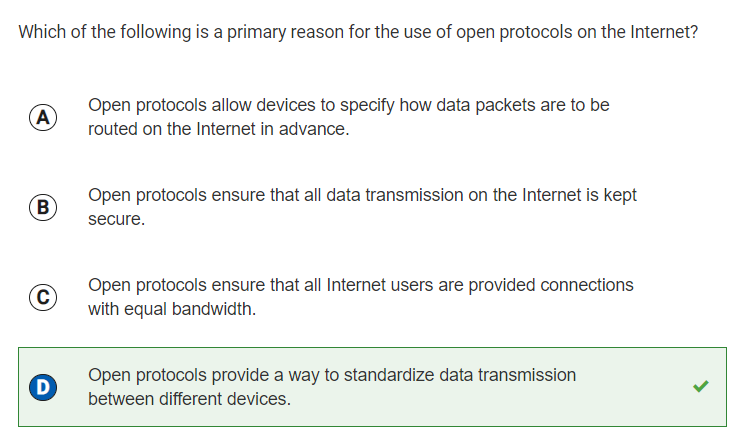
Reflection: I researched what an open protocol was in order to answer this question. After I did some research, I was able to learn that open protocols on the internet allow devices manufactured by different companies in a standardized way. This allows data transmission to be standardized between different devices, and thus D is the correct answer.
-
Q19: Adding numbers in 4-bit representation

Reflection: For this question, I consulted my peers for help, because I didn’t know much about binary sequences or “bits.” I learned that “bits” are the 1s and 0s that come together to form a decimal number in binary. I also learned that the largest number 4 bits can represent is 15, and this knowledge helped me understand this question. While 14 and 15 can be represented by 4 bits, their sum, 29, cannot be represented because the largest number that can be represented by 4 bits is 15.
-
Q20: Bits needed to represent directions
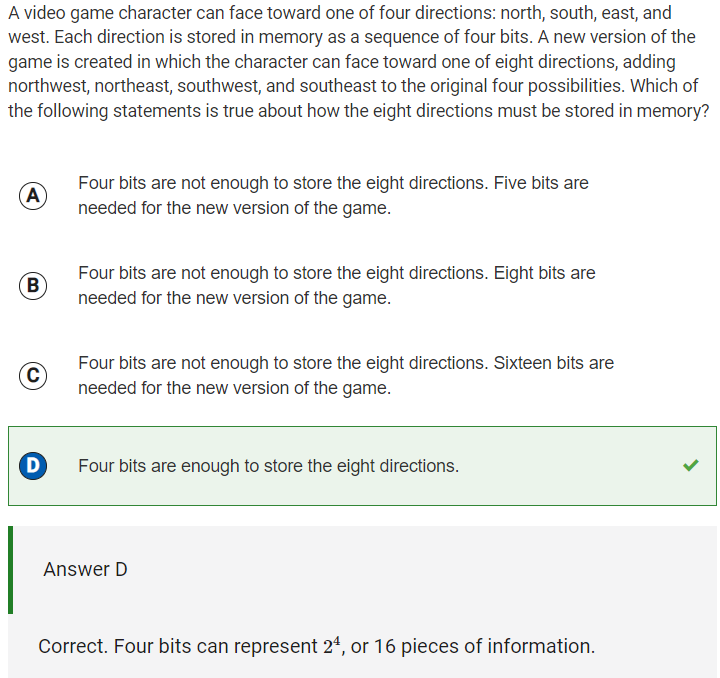
Reflection: The collegeboard answer explanation helped me understand this problem better after I answered it. I learned that 4 bits can store 16 pieces of information (24 = 16). Because the developer is trying to store only 8 directions for the character, 4 bits should be enough to store the directions because 8 < 16.
-
Q20: Data that can be represented with binary sequences
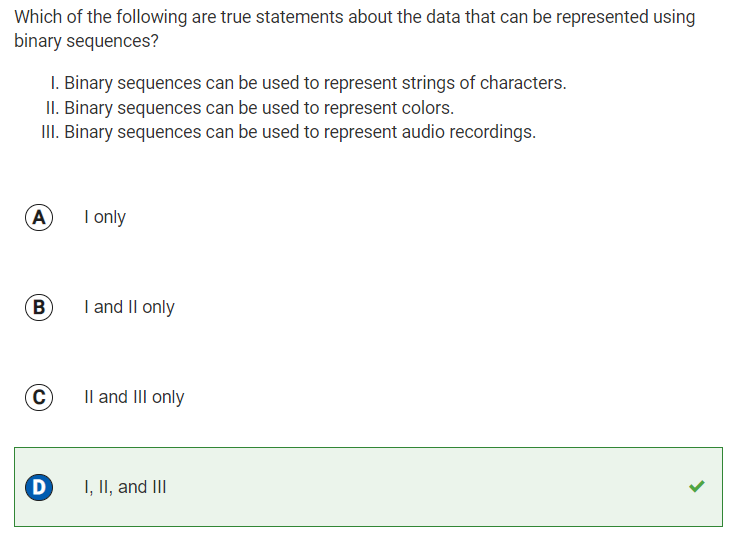
Reflection: I am blogging this question because prior to it, I didn’t know a lot about binary sequences. Now I know that digital data is represented at the lowest level by sequences of bits, which is essentially binary sequences. I also learned that binary sequences can be used to represent many different kinds of data, such as text (strings of characters), colors, numbers, images, and sounds (audio recordings).
-
Q22: Decimal value not equal to given binary values
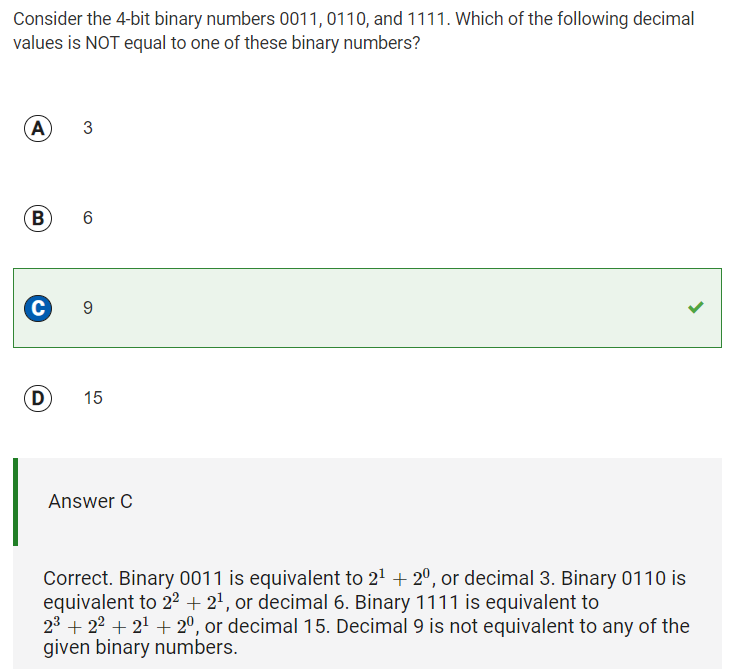
Reflection: I had to look this problem up, because I don’t know much about binary numbers.
-
Q23: Digital representation of position of runner
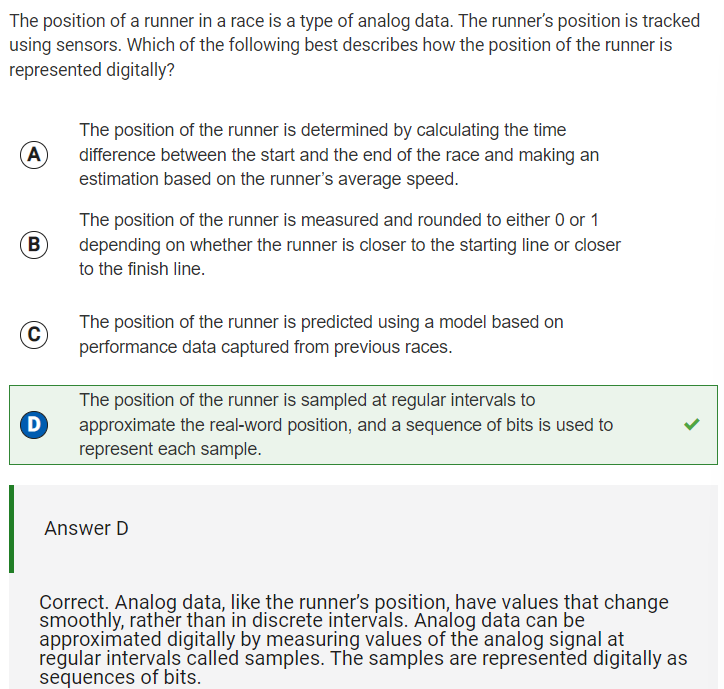
Reflection: From this I learned that analog data is sampled at multiple points and has a continuous electric signal, while digital signals have non-continuous electrical signals. At first I didn’t know how to answer this question, but reading the collegeboard explanation after completing the test gave me some insight. Analog data values change smoothly and are sampled at regular intervals, and therefore the position of the runner must be sampled at regular intervals to approximate the real-world position. The analog data can be approximated digitally by mearuding the analog signal at intervals called samples. Sequences of bits are used to represent the samples digitally.
-
Q24 Put binary and decimal numbers in order
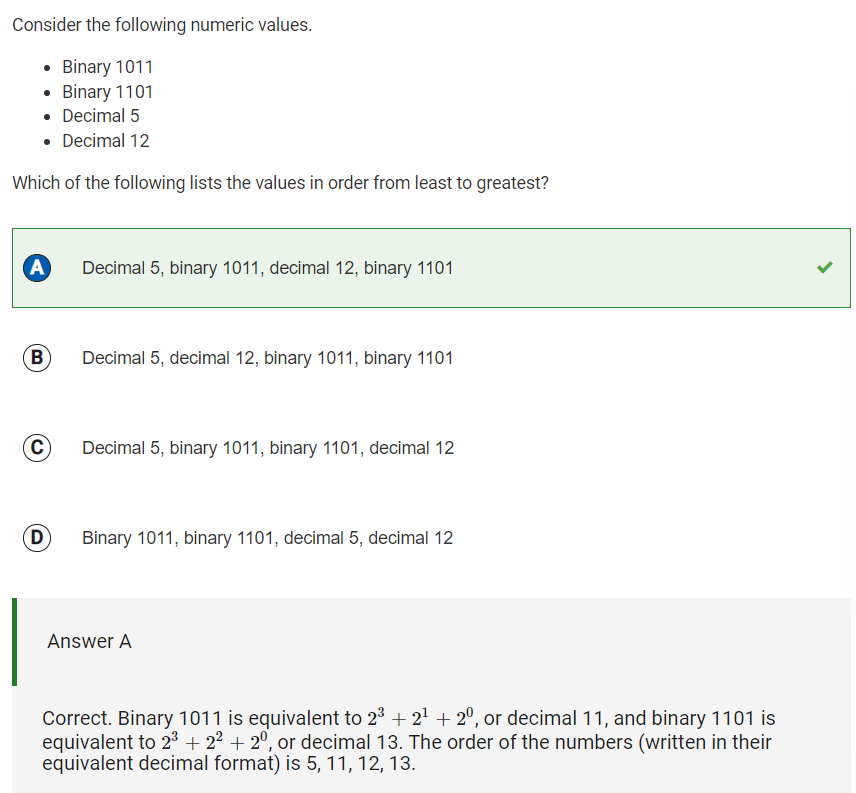
Reflection: I had to look up what decimal number binary 1011 stands for, and discovered that it was equivalent to 11. I also looked up what decimal number binary 1101 stands for, and discovered that it was equivalent to 13. Then, I simply ordered the numbers from least to greatest: 5, 11, 12, 13, or 5, 1011, 12, 1101.
-
Q26 Appropriate data type for isOpen
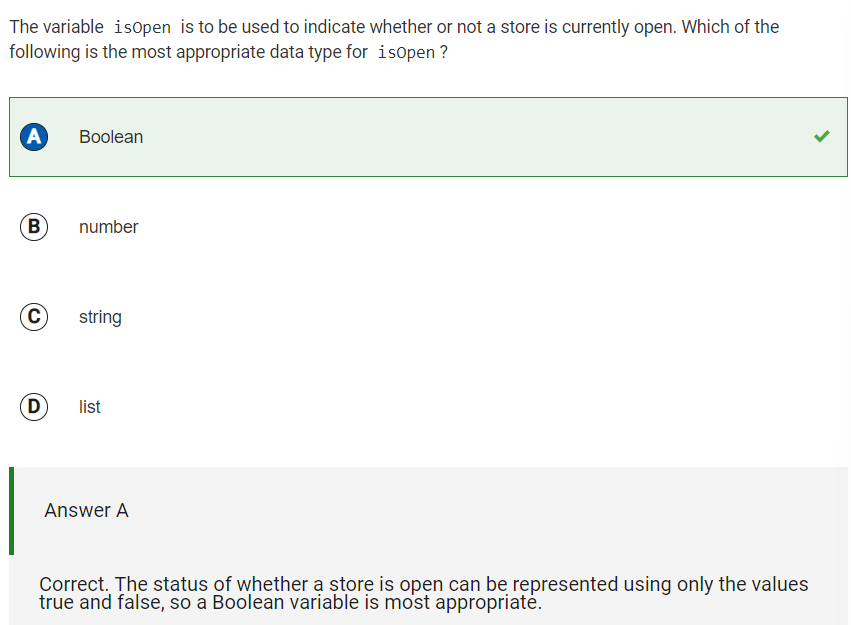
Reflection: For this question, I had to keep in mind the fact that a Boolean variable is one that is represented by the values true and false. Because whether or not a store is currently open can be represented by a true/false statement, the most appropriate data type for isOpen would be a boolean.
-
Q29 Benefit of using a list as a data abstraction
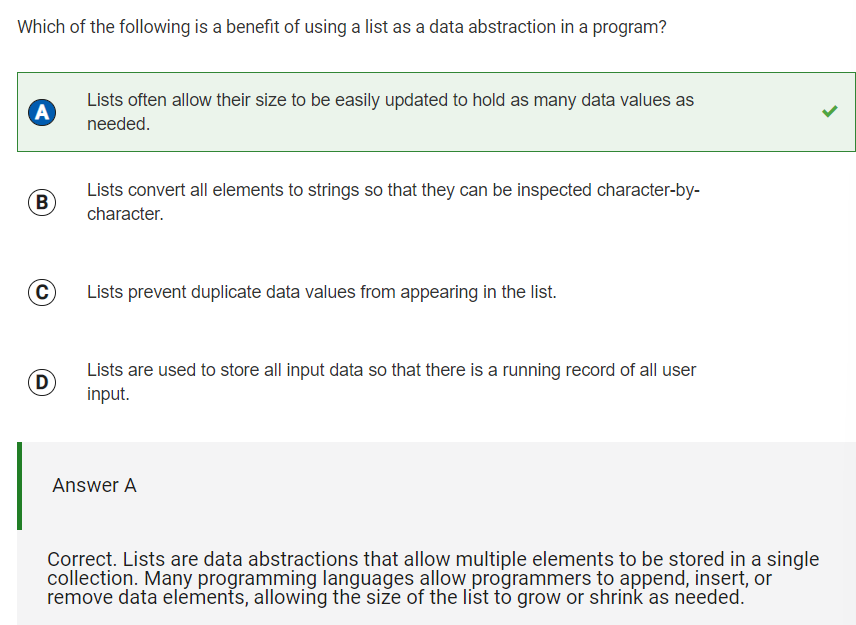
Reflection: From this question, I learned that lists are best used in data abstraction in a program, because they can hold many data values and can be easily changed as needed. From Question #30, it is also easy to apply the same algorithm to every element in a list than it is to apply an algorithm to many variables separately
-
Q32 Contents of myList and yourList
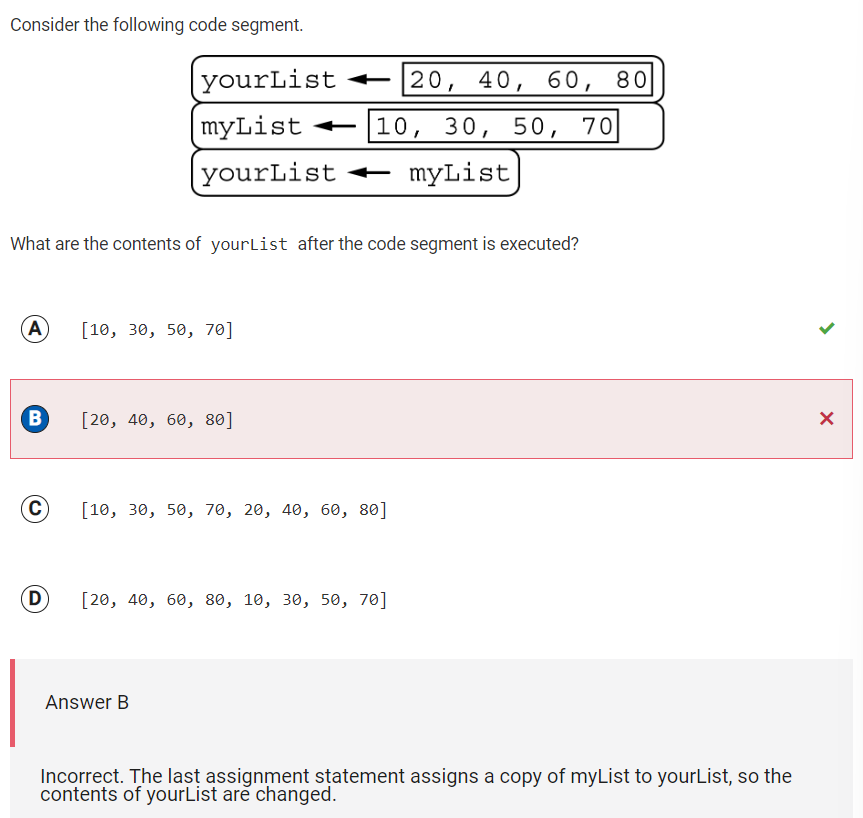
Reflection: For this question, I answered B while the correct answer was A. This is because myList was converted to have the contents of yourList – myList had the values of [10, 30, 50, 70], but now that it’s been converted to have the contents of yourList, it will no longer have [10, 30, 50, 70]. Therefore, A is the correct answer.
-
Q36 Store even numbers in evenList
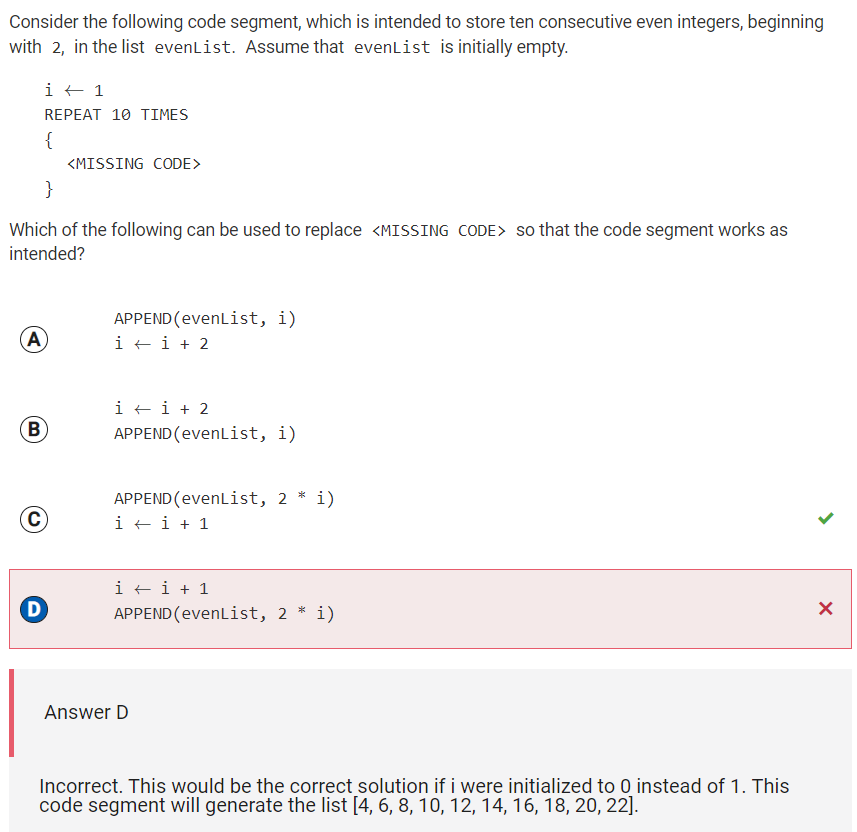
Reflection: Option C is correct, because it would store the first element of the list as 2, while the option D would store the first element of the list as 4.
-
Q38 Update values of three words
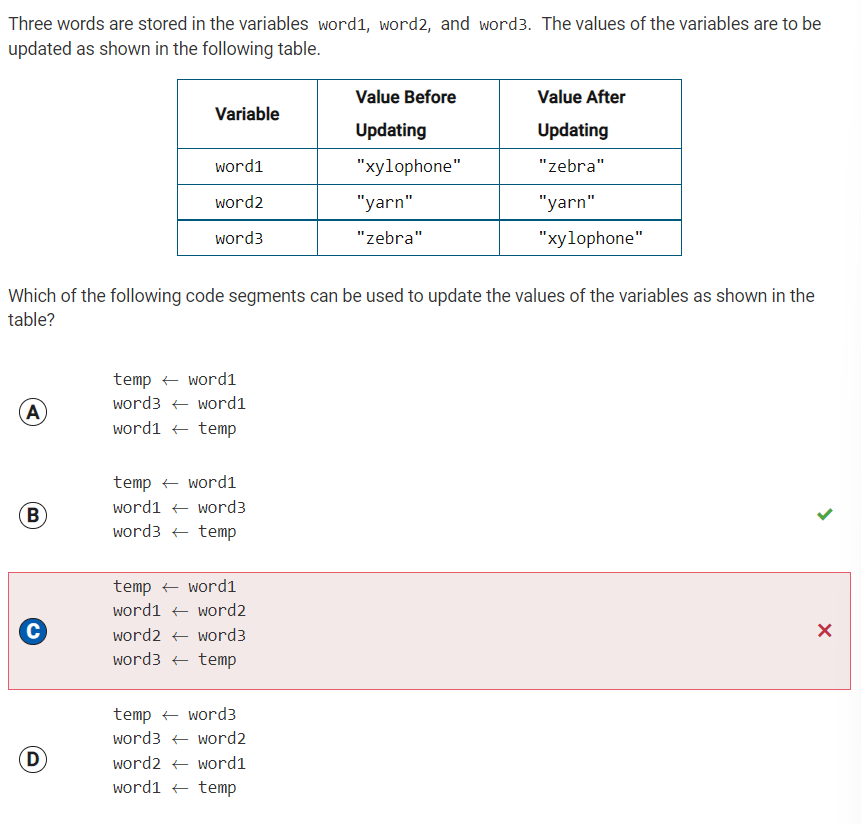
Reflection: Option B is correct, because the first statement assigns the value of word1 to the temporary variable temp. The second statement assigns the value of word3 to word1. The third statement assigns the original value of word1, which is stored in temp, to word3. The original values of word1 and word3 are interchanged, which reverses the values of the variables as intended, making the table values after updating zebra –> yarn –> xylophone.
-
Q39 Valid index for wordList
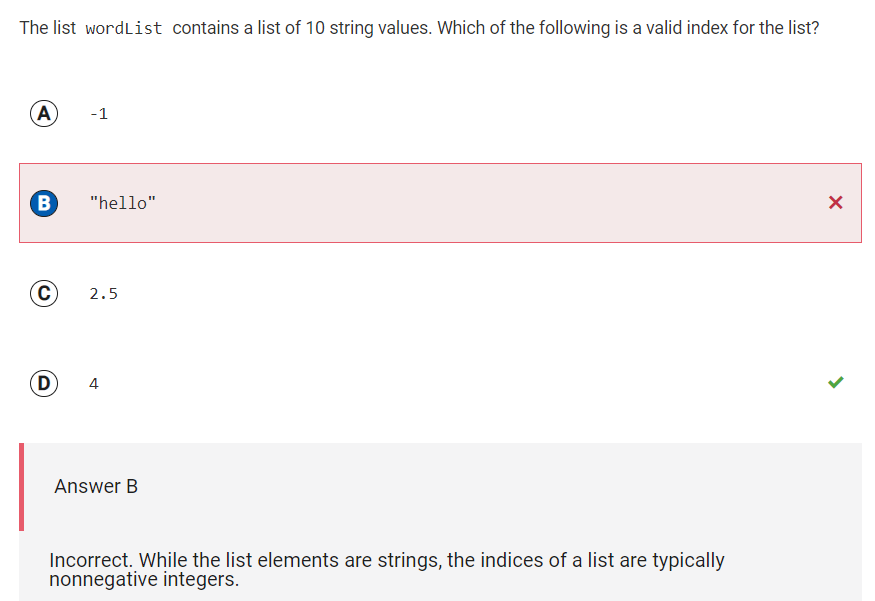
Reflection: I learned that indices are usually non-negative integers. “Hello” is a string value, which could be an element in the list. A list is a structure whose index values are 1 through the number of elements in the list. The list’s index, however, should be a non-negative integer, and be between 1 and 10, because there are 10 elements in the list. 4 is a non-negative integer and 1<4<10, and thus option D is correct.
-
Q43 Value of x after REPEAT UNTIL block
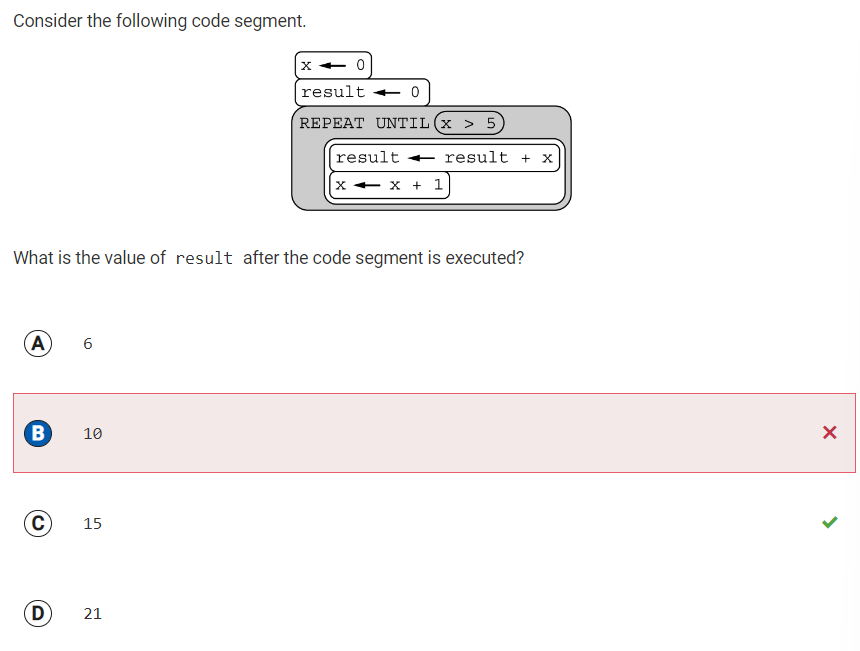
Reflection: I chose option B, which would be the value of result if the loop iterated one less time. The variables x and result are both initialized to 0. Within the loop, result is increased by x and x is increased by 1. The loop stops when x>5. So, the result must be the sum of the integers from 0 to 5, which is 15.
-
Q47 Values of variables after arithmetic operations
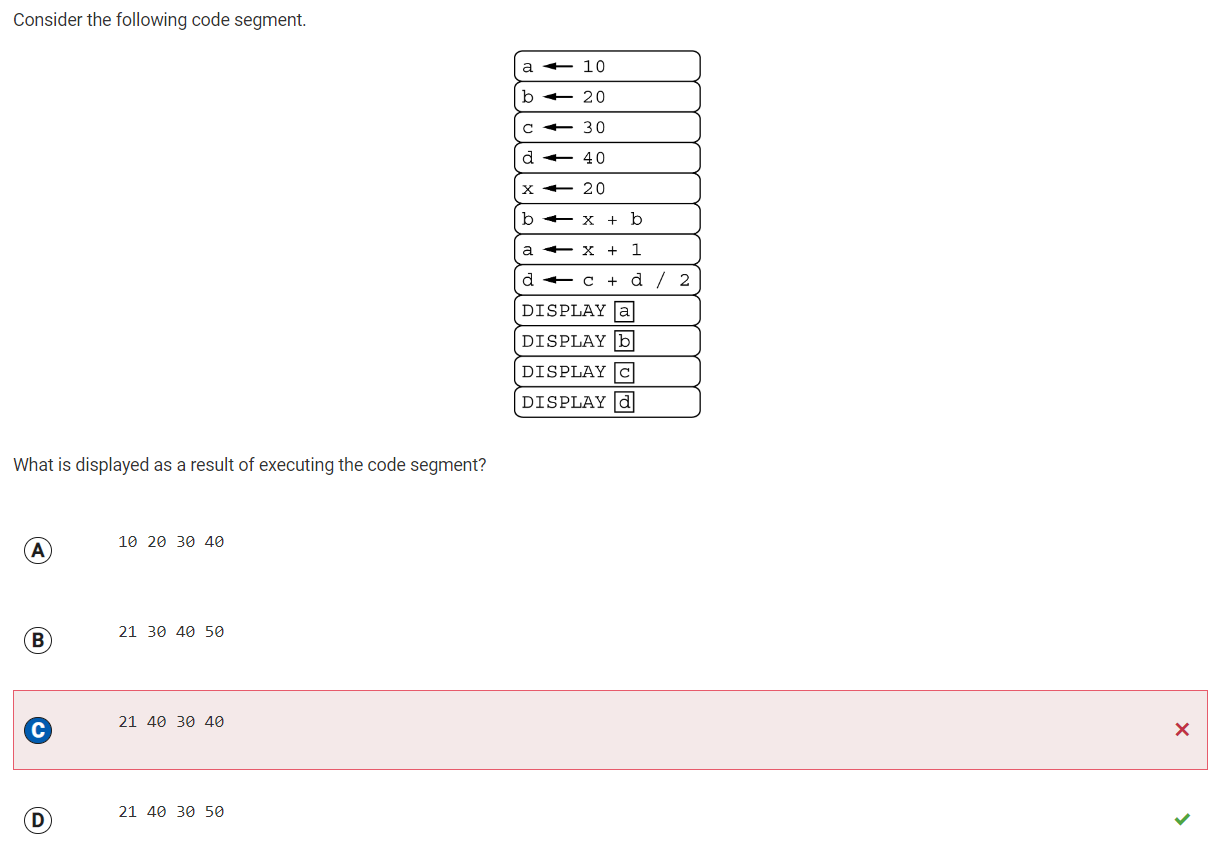
Reflection: For this question, I did the order of operations wrong. For the 8th code block, the operation is c + (d/2). However, I thought that it was (c+d)/2. C is 30, and d is 40. 30 + (40/2) = 50, therefore, the correct answer is option D.